What is Velocity?
Velocity is a measure of how fast an object moves in a specific direction over time. In simple terms, it tells us how quickly something is moving and in which direction.
Since velocity depends on both speed and direction, it is called a vector quantity. This means just knowing the number (speed) is not enough you also need to know the direction of movement.
The SI unit of velocity is meters per second (m/s), but it can also b...
What is Velocity?
Velocity is a measure of how fast an object moves in a specific direction over time. In simple terms, it tells us how quickly something is moving and in which direction.
Since velocity depends on both speed and direction, it is called a vector quantity. This means just knowing the number (speed) is not enough you also need to know the direction of movement.
The SI unit of velocity is meters per second (m/s), but it can also be expressed in kilometres per hour (km/h) or miles per hour (mph).
Difference Between Velocity and Speed
While speed and velocity are related, they are not the same:
Speed: Speed is a scalar quantity, meaning it only tells us how fast an object is moving, without specifying direction.
Velocity: Velocity is a vector quantity, meaning it tells us both how fast and in which direction the object is moving.
Some key points:
- Speed measures the rate of change of distance, while velocity measures the rate of change of displacement.
- Speed is always positive or zero, but velocity can be positive, negative, or zero depending on the direction of motion.
Average Velocity
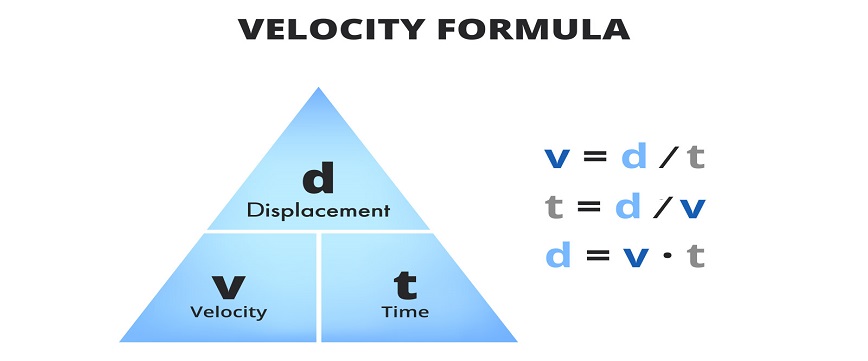
Average velocity is the total change in position (displacement) divided by the total time taken.
"Average Velocity"="Change in Position (Displacement)" /"Change in Time"
Example: If your office is 10 kilometres away and it takes 15 minutes to reach, your average velocity can be calculated as follows:
Convert 15 minutes into hours: 15" minutes"=0.25" hours"
Average velocity: V = 10 km/ 0.25 hours =40 km/h
This means your car moves at an average speed of 40 km/h in the direction of your office. Initial and Final Velocity
Initial Velocity (u): The speed at which an object starts moving.
Final Velocity (v): The speed and direction of an object after it has accelerated or decelerated.
The final velocity can be calculated using the formula: v = u+(a*t)
Where:
u = Initial Velocity
a = Acceleration
t = Time
Example: If a car starts with an initial velocity of 2 m/s and accelerates at 3 m/s² for 1 second, the final velocity will be: v=2+3=5 m/s
Constant Velocity
An object moves with constant velocity when it travels at the same speed in the same direction. In other words, the motion is in a straight line without changing speed.
Velocity helps us understand not just how fast an object moves, but also where it is heading, making it a crucial concept in physics and daily life.